Today’s historians know a lot about the rise and fall of famous empires, but fewer people know about some of the more mysterious cultures from history.

These lesser-known societies are often forgotten because they didn’t leave behind massive stone monuments like the pyramids, or impressive stone calendars like the Mayan temples. But these ancient cultures have left just as much impact on world history as any other society.
The following list shares 8 lesser-known ancient civilizations that you probably don’t know much about. These aren’t all cultures that were “lesser” than others by any measure. Rather, these are groups whose stories have been forgotten in recent centuries.
Ethiopia’s Kingdom of Aksum

People now tell stories about the kingdom of Aksum in Ethiopia. Some people say it’s the lost kingdom of the Queen of Sheba, while others say it’s where the Ark of the Covenant will rest for good. A philosopher said it was one of the four best kingdoms in the world. It did well for a long time after Rome fell. Eskom’s main trade advantage over its neighbors was taken away, and the Zagwe dynasty took its place.
The Kingdom of Kush
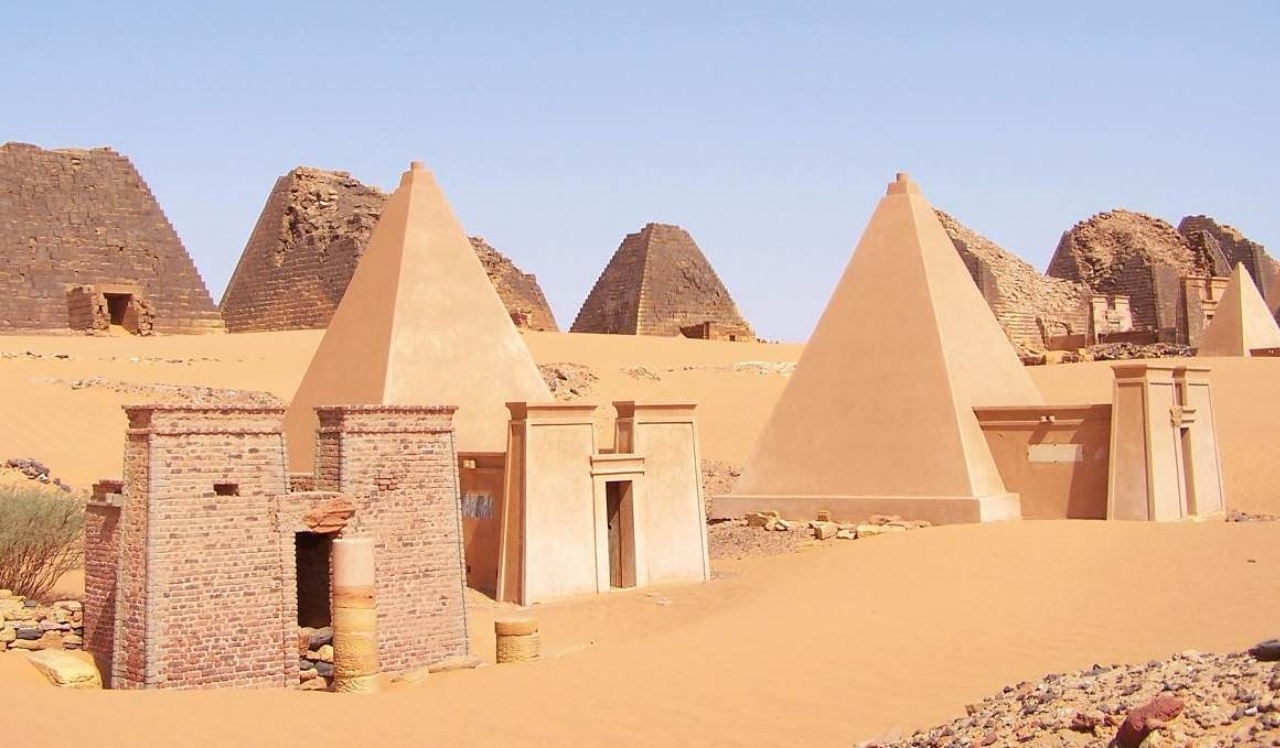

Around 8000 BC, the Kush Kingdom began. As early as 2000 BC, Kush had a complex, stratified society that was kept going by large-scale farming. Egypt, to the north of Kush, took advantage of it and took it over. Then Kush took Egypt back and became even stronger than the Egyptians. They ruled Egypt for over a thousand years and helped build up Sudan.
They made what is called “Meroitic” writing. Most of their history is unknown because their script hasn’t been translated.
The Nok
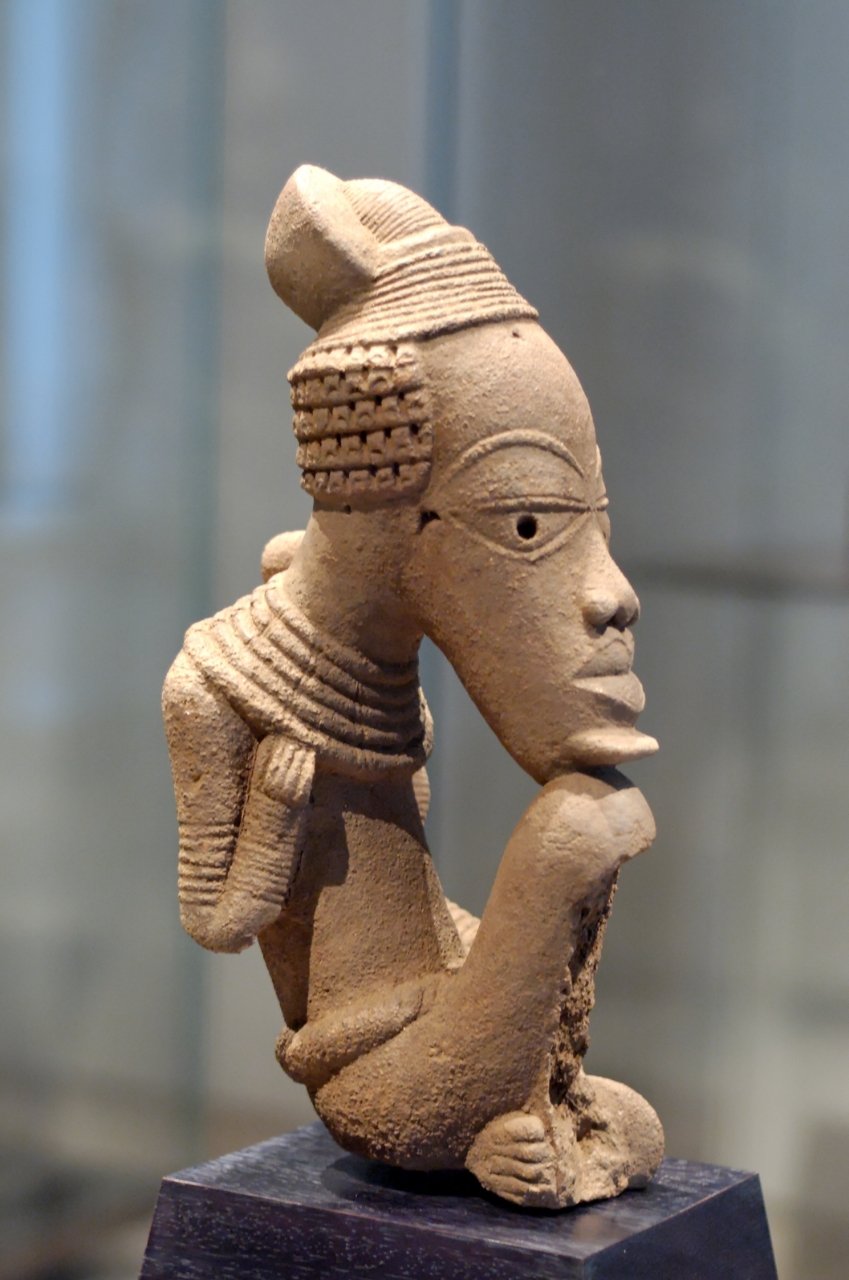

From about 1000 BC to 300 AD, the mysterious Nok lived in what is now northern Nigeria. During a tin mining job in 1943, evidence of the Nok was found by accident. Miners found a terra-cotta head, which hints at a long history of sculpture. Since then, more detailed terra-cotta sculptures have been made, showing people with fancy jewelry and carrying batons and flails (symbols of authority also seen in ancient Egyptian art). People with diseases like elephantiasis are shown in other sculptures.
Artifacts have often been taken out of their original setting without archeological analysis, which adds to the mystery of the Nok. In 2012, a group of Nok figurines stolen from Nigeria’s national museum and smuggled into the U.S. was given back to that country.
The Land of Punt
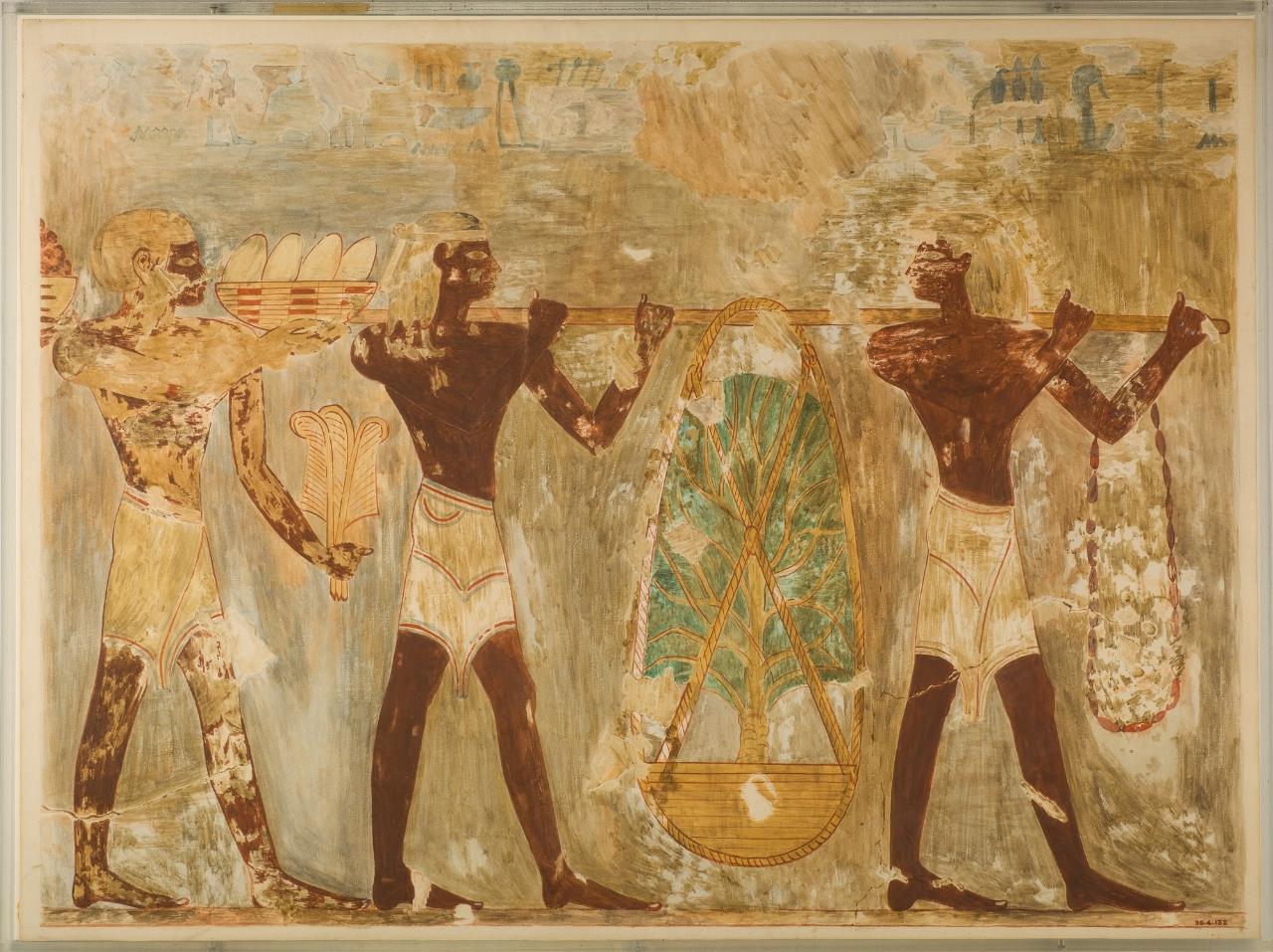

Most of what we know about some cultures comes from what other cultures have written down. This is the case with Punt, a mysterious African kingdom that traded with the ancient Egyptians. Since at least the 26th century BC, when the pharaoh Khufu was in charge, the two kingdoms traded goods.
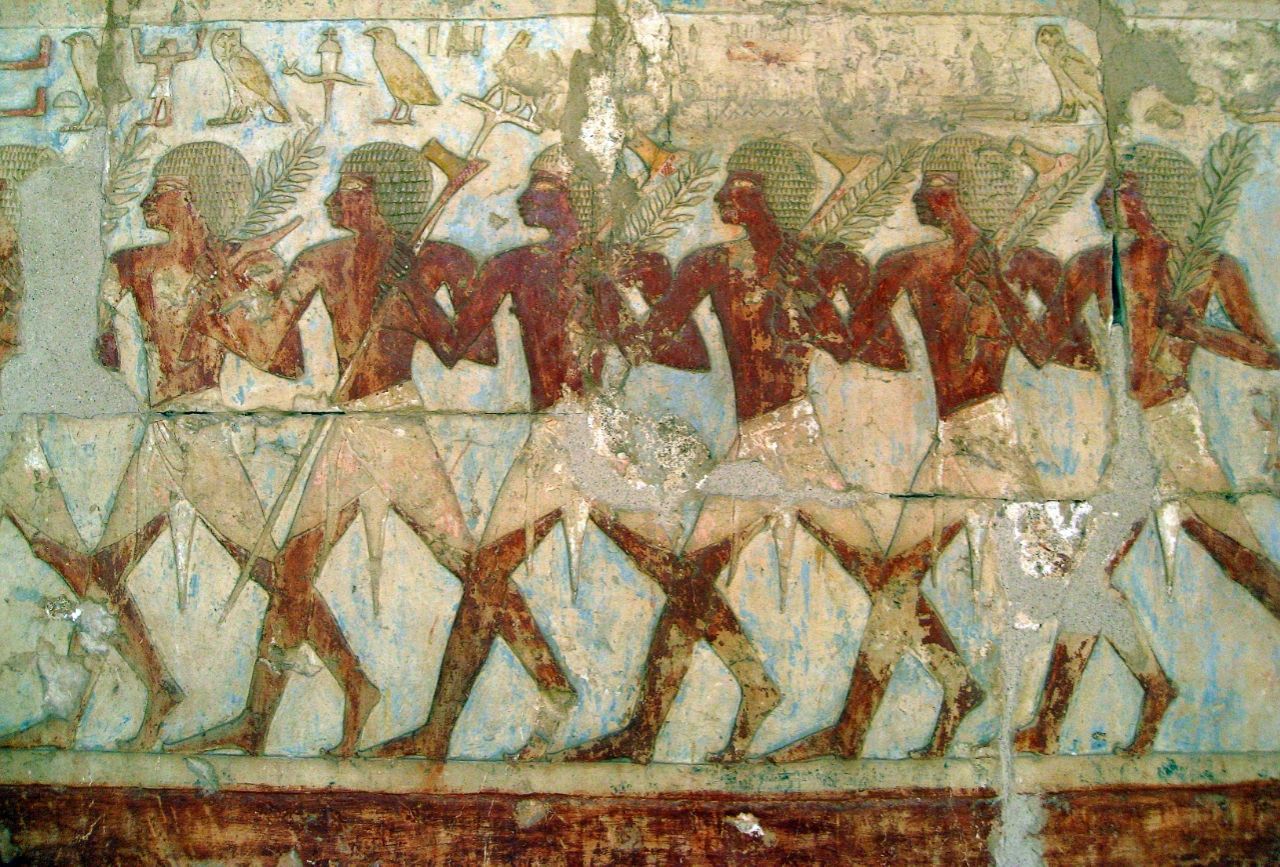

No one knows where Punt was, which is strange. The Egyptians wrote a lot about the gold, ebony, and myrrh they got from Punt and the sea trips they sent to the lost kingdom. But the Egyptians won’t say where all these ships were going, which is frustrating. Scholars think that Punt could have been in Arabia, on the Horn of Africa, or along the Nile River near where South Sudan and Ethiopia meet today.
The Etruscians
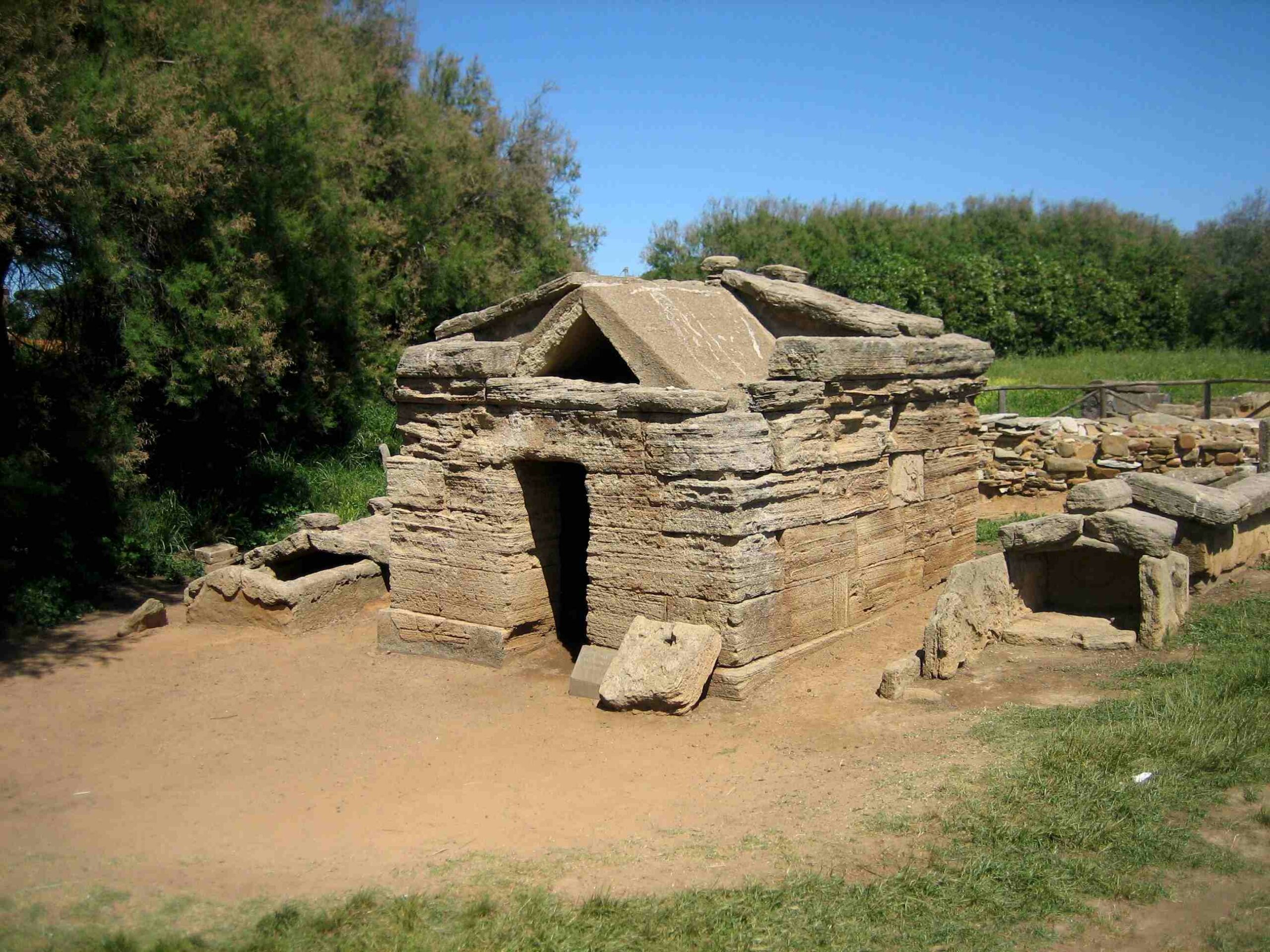

The Etruscians were a group of people who lived in northern Italy from about 700 BC to 500 BC when the Roman Republic began to take over. They came up with their way of writing and left behind opulent family tombs, including one for a prince found in 2013.
At the Etruscan sanctuary of Poggio Colla, the oldest picture of a woman giving birth in Western art was found. It shows a goddess squatting to give birth. At the same site, archaeologists found a sandstone slab 4 feet by 2 feet (1.2 by 0.6 meters) with rare Etruscan writing on it.
The culture of the Aztecs
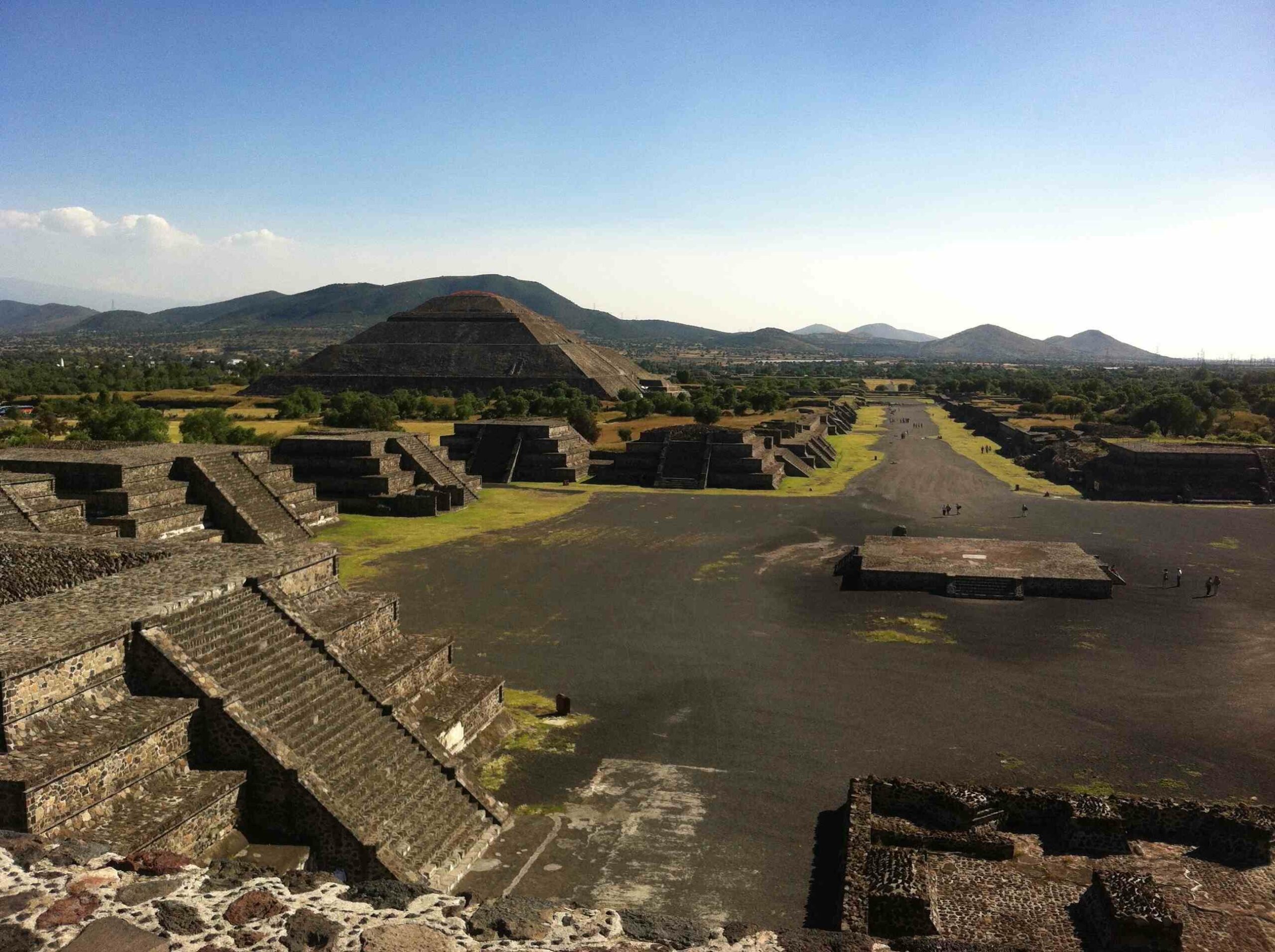

Nearly at the same time, the Incas became powerful in South America, and the Aztecs came to power. People in what is now Mexico lived in three big rival cities in the 1200s and early 1300s. These cities were Tenochtitlan, Texcoco, and Tlacopan.
Around 1325, these rivals came together to form a new state, ruling the Valley of Mexico. Back then, people liked the name Mexica better than the name Aztecs.
The Mayans, a powerful civilization in Mexico and Central America, fell about a hundred years before the Aztecs took over.
The military power base was in the city of Tenochtitlan, which became the spearhead for the conquest of new land. However, the Aztec emperor didn’t have direct control over every city or region. Local governments stayed in place and were forced to pay the Triple Alliance different amounts of tribute.
The Aztecs were at the height of their power in the early 1500s. Then, though, the Spanish came. As a result, the Spanish conquistadors and the Native American allies they had gathered fought under the command of Hernan Cortes (1521). The once-great Aztec Empire finally fell because they lost this decisive battle.
The Romans and their culture
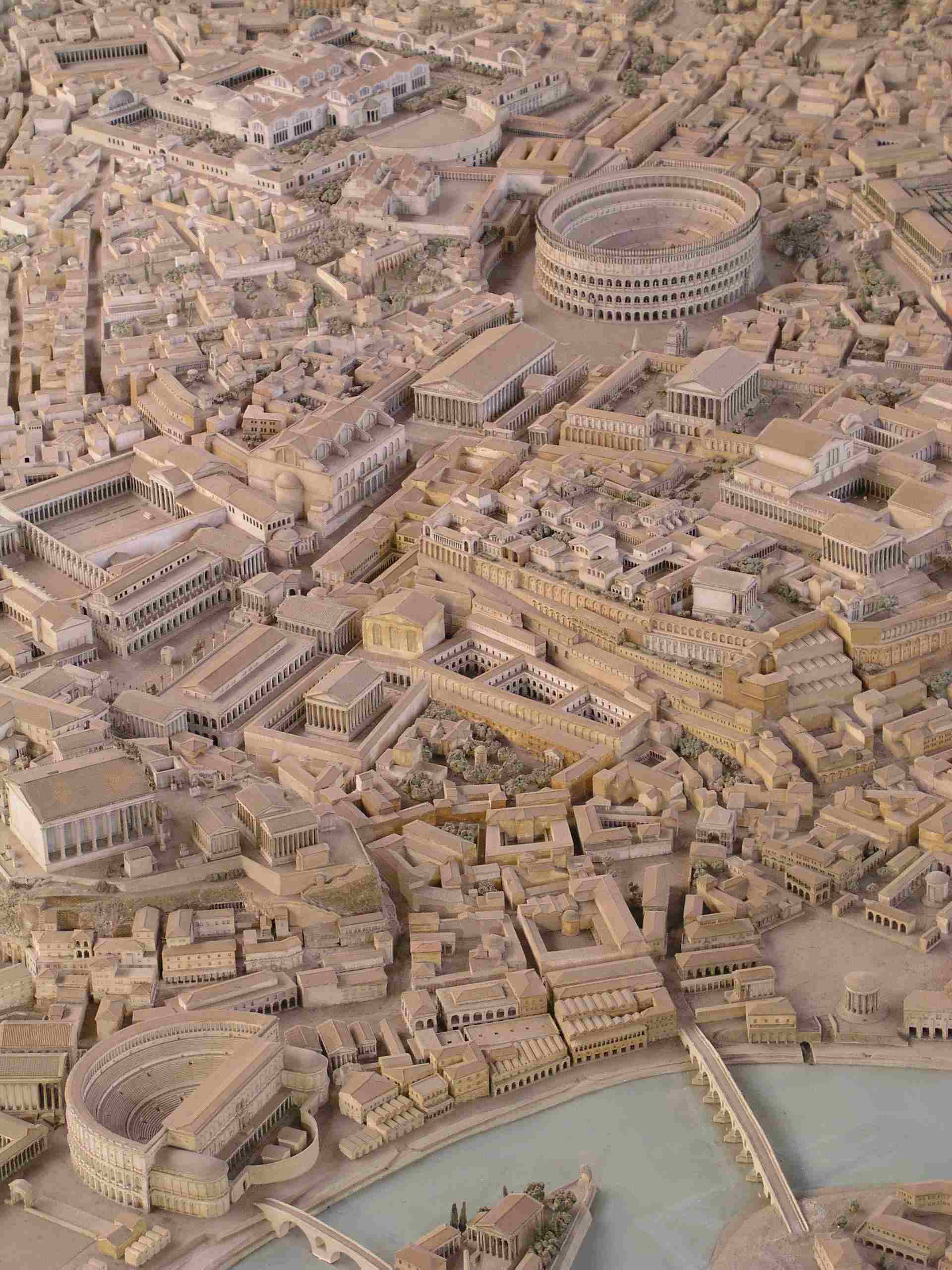

Around 600 BC, the Roman civilization began to grow. Even the story of how ancient Rome came to be consists of legends and myths. The Roman Empire ruled over a huge land area when it was at its strongest. All the countries that are now in the Mediterranean were part of ancient Rome.
In the beginning, Rome was run by kings, but after only seven of them, the people took control of their city and started running it themselves. They made a group of people calls the Senate to rule over them. After this, Rome became known as the Roman Republic.
Some of the best rulers in history, like Julius Caesar, Trajan, and Augustus, rose to power and then lost it. But in the end, the empire grew so big that just one person could no longer rule it.
In the end, barbarians from northern and eastern Europe swarmed into the Roman Empire and took over.
The civilization of the Persians
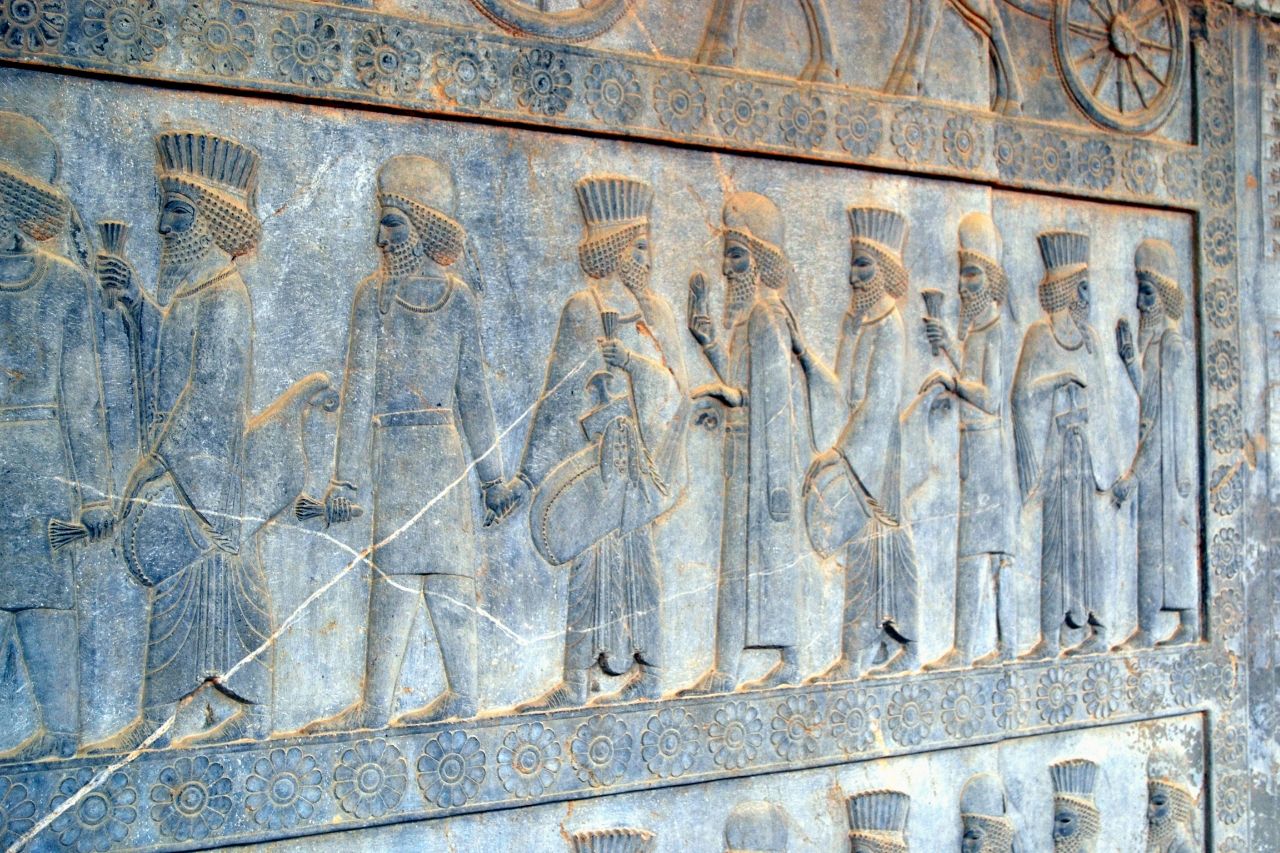

The ancient Persian civilization once held the title of the most powerful empire on Earth. Even though they were in charge for over 200 years, the Persians took over two million square miles of land. From the south of Egypt to parts of Greece and India, the Persian Empire was known for its strong military and wise leaders.
Before 550 BC, when they built such a big empire in just 200 years, the Persian Empire, known then as Persis, was split into groups led by different people. But then, King Cyrus II, who was later called Cyrus the Great, took over. He united the whole Persian kingdom and then went on to conquer ancient Babylon.
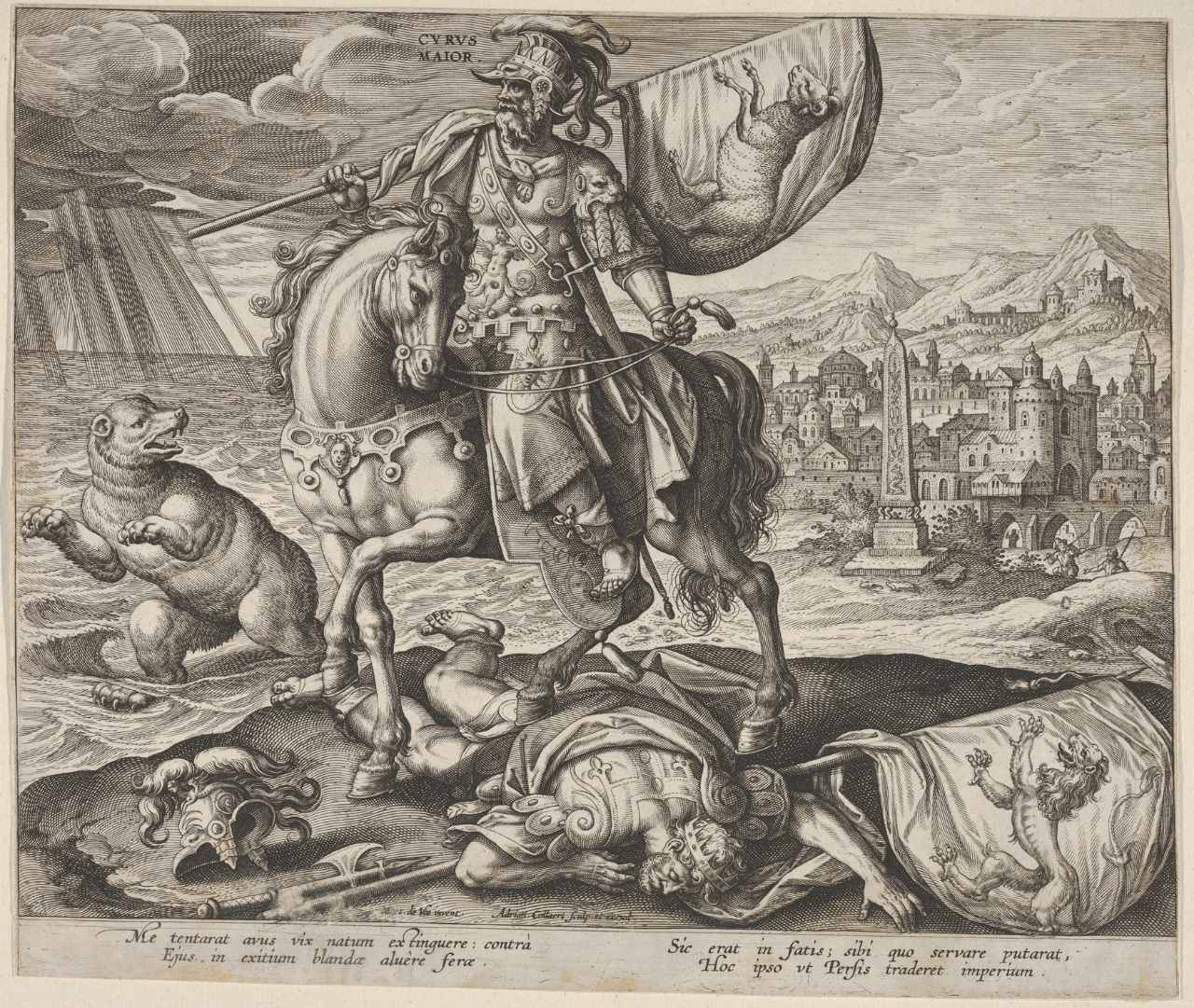

It has been estimated that he took over a hundred places in 533 BC, including India, which is far away in the east. Even after Cyrus died, his descendants kept expanding cruelly and fought with the brave Spartans in the now-famous battle.
Ancient Persia ruled over all of central Asia and Egypt at its peak. This changed in 330 BC when a famous Macedonian soldier named Alexander the Great brought the whole Persian Empire to its knees and ended that civilization.