Toumaï is the name given to the first fossil representative of the Sahelanthropus tchadensis species, whose practically complete skull was found in Chad, Central Africa, in 2001. Dated around 7 million years ago, Toumaï is believed to be the oldest hominid known to date.

Discovery Of Toumaï
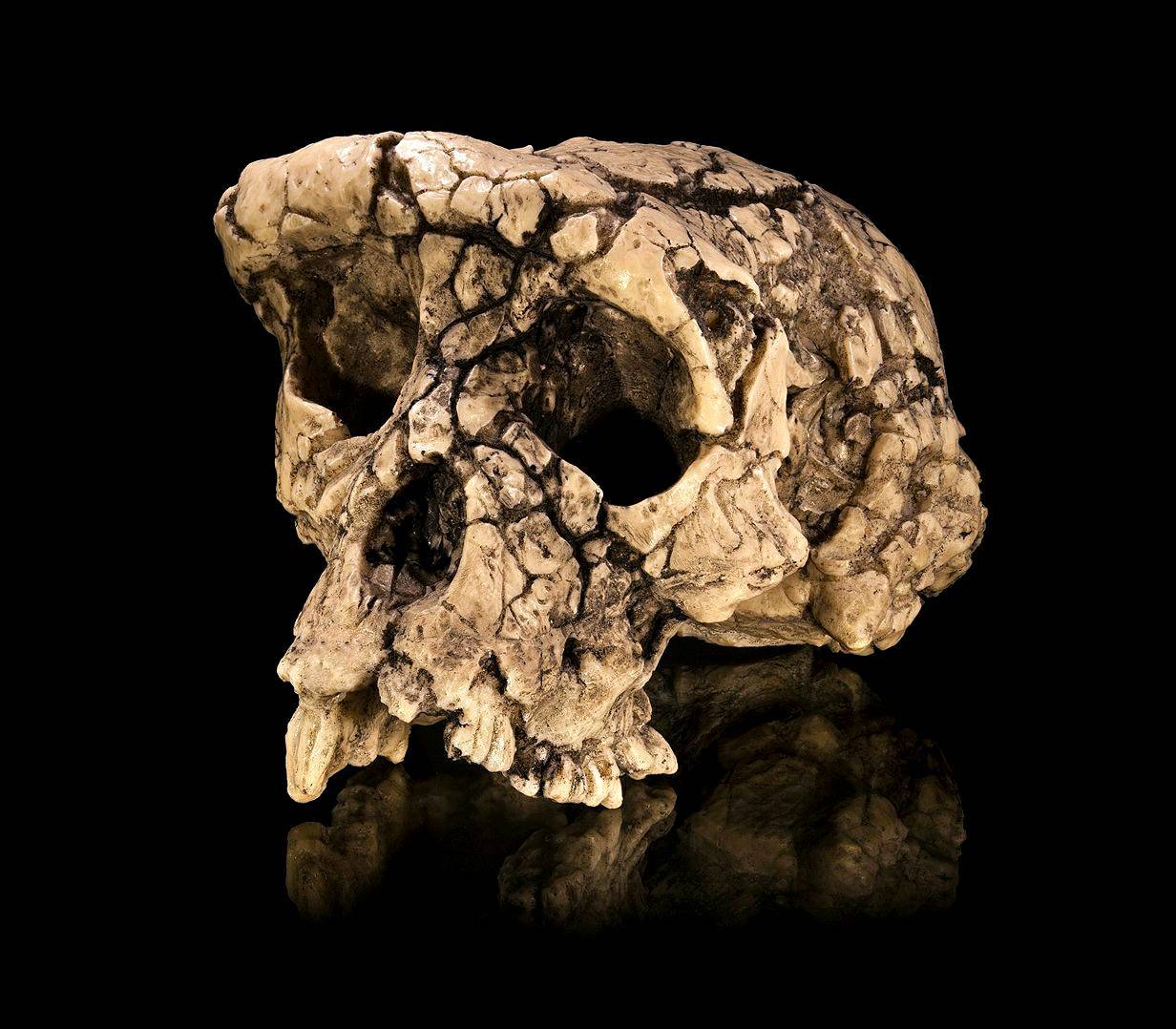
In 2001, researchers made an extraordinary discovery in Northern Chad’s desert landscape: a collection of bones and bone fragments sitting beside a mostly complete skull. Researchers named the skull “Toumaï,” which means “hope of life” in the language of the Toubous, or Goranes, a nomadic population living in Chad.
The skull’s features were a mashup of old and new, a chimp-sized brain but with small canine teeth — they’re typically smaller in hominins than in chimps, our nearest living relatives.
It was the fossil’s age that was even more shocking, however. Toumaï is between 6 million and 7 million years old. At the time, paleoanthropologists believed that the last common ancestor we share with chimps was at least a million years younger. Toumaï suggested the split in our lineages occurred much earlier than thought.
Dated around 7 million years ago, Toumaï is believed to be the oldest hominid known to date. It would shortly precede the divergence between chimpanzees and the human line. It is said to be a male weighing 35kg and measuring around one meter, who would have lived in a forest near a water point, as suggested by the fossils of fish, crocodiles and monkeys found near him.
Hominid Vs Hominin
Hominid – the group consisting of all modern and extinct Great Apes (that is, modern humans, chimpanzees, gorillas and orang-utans plus all their immediate ancestors).
Hominin – the group consisting of modern humans, extinct human species and all our immediate ancestors (including members of the genera Homo, Australopithecus, Paranthropus and Ardipithecus).
Toumaï And The “East Side Story” Theory
The discovery of Toumaï in the Djurab desert in Chad, nearly 2,500 km west of the Great East African Rift Valley, which is nicknamed the “Cradle of Humankind”, casts doubt on the “East Side Story” theory. Proposed by the paleoanthropologist Yves Coppens, this hypothesis states that the ancestors of homo sapiens would have appeared in East Africa following geological and climatic upheavals.
Researchers Suggest Toumaï Could Be A Bipedal Primate!
For some anthropologists, Toumaï would even be a bipedal primate and would be one of the first ancestors of the human line. Bipedal primate means Toumaï may have walked on two legs. However, because no bones or bone fragments below the skull (postcranial remains) have been discovered, it is not known definitively whether Toumaï was indeed bipedal, although claims for an anteriorly placed foramen magnum suggests that this may have been the case and Toumaï was indeed one of us.
The foramen magnum is the opening at the base of the skull where the spinal cord exits. The angle of the opening can reveal if the spine stretched out behind the skull, as it does for four-legged animals, or dropped down, like it does for bipedal hominins. For other experts, on the contrary, it would only be an ape and not a hominin at all. But, is it that??